How Saylor Is Building Intelligent Leverage with Bitcoin-Backed Perpetual Preferred Stocks

Executive Summary: The Pioneering of Bitcoin-Backed Corporate Finance
The company's strategic pivot from conventional convertible debt to a tiered family of perpetual preferred stocks represents a fundamental innovation in corporate finance. By intelligently leveraging its substantial Bitcoin treasury as a form of pristine collateral, the company has not only secured a permanent and scalable source of capital but has also engineered a new class of financial instruments with superior credit profiles and capital efficiency. This is quantitatively demonstrated through the company's proprietary financial models, including its BTC Torque and BTC multiple frameworks.
The analysis reveals that the company's prior reliance on convertible debt, while initially successful due to low coupons, introduced systemic vulnerabilities such as looming refinancing pressure, delta-hedging headwinds, and market illiquidity. The new perpetual preferred stock model, exemplified by the flagship STRC, directly addresses and eliminates these risks, offering a permanent, high-yield, and highly liquid alternative. Quantitative modeling confirms that these preferred securities generate significantly higher BTC Torque than common equity or convertible notes, a metric that measures the effectiveness of capital raises in creating long-term shareholder value.
Section 1: The Strategic Evolution of Capital Financing
1.1 From Convertible Debt to Perpetual Preferreds: A Paradigm Shift
The company's journey in financing its substantial Bitcoin treasury began in 2020 with a dual-pronged approach. This strategy initially relied on a combination of at-the-market (ATM) common stock sales and the issuance of convertible senior notes. This method proved effective in accumulating capital for early Bitcoin acquisitions. By year-to-date 2025, the company had raised $6.6 billion via ATM sales of its Class A common stock and an additional $2.0 billion through convertible debt offerings. The convertible notes were particularly noteworthy for their remarkably low interest rates, with some tranches carrying coupons as low as 0%. For a time, this seemed to be a highly advantageous and cost-effective way to secure significant capital.
However, this reliance on fixed-term debt instruments introduced strategic shortcomings that would eventually prompt a profound shift in the company's approach to capital financing. The convertible bonds, despite their low headline interest rates, were encumbered by fixed maturity dates. This created a critical vulnerability: a looming obligation to repay the principal in full if the stock price did not rise sufficiently to trigger conversion into equity. Such a scenario could potentially force the company to sell Bitcoin at inopportune times or necessitate new debt issuances simply to pay off old ones, a perpetual cycle of refinancing risk.
Beyond the maturity risk, the company observed a more insidious and systemic issue with its convertible debt. Executive Chairman Michael Saylor identified a "delta-hedging headwind" created by institutional investors who purchased the notes. These investors often engage in dynamic hedging, which involves shorting the company's common stock (MSTR) to manage their risk exposure as the bond's conversion option moves in or out of the money. This activity creates a persistent downward pressure on the share price, effectively increasing the "true" cost of capital beyond the nominal coupon rate. Saylor estimated this hidden cost could approach 12% when accounting for dilution and market dynamics. Furthermore, these convertible bonds were largely illiquid, trading in a closed ecosystem of a small group of institutional investors. This constrained the company's ability to raise capital at scale and limited its buyer base, highlighting a fundamental strategic flaw. The introduction of a new family of perpetual preferred stocks was a direct, engineered response to these very shortcomings. The new securities, by design, do not have a maturity date, eliminating refinancing risk and offering a permanent capital solution.
Section 2: The Bitcoin Treasury Financial Lexicon
2.1 Defining the Core Metrics for a Bitcoin-Centric Business
Traditional financial metrics, such as Price-to-Earnings (P/E) or Enterprise Value-to-EBITDA, are ill-equipped to capture the unique dynamics of a company that holds a significant portion of its treasury in a volatile, appreciating asset like Bitcoin. The company's earnings reports are dominated by unrealized gains and losses from its Bitcoin holdings, rendering conventional valuation metrics less useful. In response to this challenge, the company has pioneered a new, more appropriate financial lexicon to transparently articulate its strategy and performance.
At the heart of this new framework are several core metrics:
- BTC NAV & mNAV: BTC NAV, or Bitcoin Net Asset Value, is defined as the market value of Bitcoin in the corporate treasury. It provides a transparent, real-time snapshot of the value of the company's core asset holdings. Building on this, mNav represents the multiple of Bitcoin NAV, calculated by dividing the company's enterprise value by its BTC NAV. The mNAV serves as a crucial strategic barometer, providing a measure of market sentiment and the premium the market places on the company’s unique Bitcoin-centric strategy. This metric is used to guide capital allocation decisions, such as determining the optimal time to issue common equity.
- BTC Yield, BTC Gain, BTC $ Gain: These are key performance indicators (KPIs) designed to measure the accretive nature of the company’s capital raises on a per-share basis.
- BTC Yield is the percentage change in the ratio of Bitcoin holdings to the number of assumed diluted shares outstanding.
- BTC Gain is the number of bitcoins held at the beginning of a period multiplied by the BTC Yield.
- BTC $ Gain is the dollar value of the BTC Gain based on the market price of Bitcoin. These metrics are not intended for traditional financial performance evaluation but rather to assess management's success in growing the Bitcoin-per-share ratio. They provide a direct answer to a fundamental question for investors: "Is this capital raise making the company's shareholders richer in Bitcoin terms?"
- BTC $ Income is the change in value of the BTC $ Gain less dividend / interest costs.
- BTC $ Value is the cumulative USD value of BTC $ Gain and BTC $ Income.
- BTC $ Equity is BTC NAV less the BTC $ Value.
- BTC Multiple is the ratio of BTC $ NAV to BTC $ Equity issued.
- BTC Capital is the proceeds used from capital raised for the purpose of investing in BTC.
- BTC Torque: This is a central metric for proving the efficiency of the company's leverage strategy. BTC Torque is defined as the ratio of BTC $ Value created to the BTC Capital invested. A high BTC Torque demonstrates that a capital raise is generating a disproportionately large amount of value for shareholders.
The development and public use of this new lexicon signal a deeper strategic commitment. It is not merely about raising capital; it is about establishing a transparent, rule-based framework that allows investors to directly evaluate the company's core strategy. This new language is essential for building confidence and attracting a wider investor base by demystifying a novel financial approach.
Section 3: Analysis of Intelligent Leverage and Value Creation
3.1 Quantifying Value Creation with BTC Torque and BTC Multiple
A core thesis of the company's financial strategy is that its perpetual preferred stocks can generate superior returns on capital when compared to its convertible notes or common equity. This is quantitatively demonstrated through the company's proprietary BTC Torque model. A comparative analysis of the various capital instruments reveals a clear relationship between the degree of dilution and the capital efficiency of a given financing.
The following table, consolidated from data in the company's Q1 and Q2 presentations, illustrates this dynamic under a "Maximalist" assumption, where the Bitcoin Annualized Rate of Return (BTC ARR) is 30% and the duration is 10 years :
Table 1: BTC Torque & BTC Multiple Comparison at 30% BTC ARR (10-Year Duration, 2x mNAV)
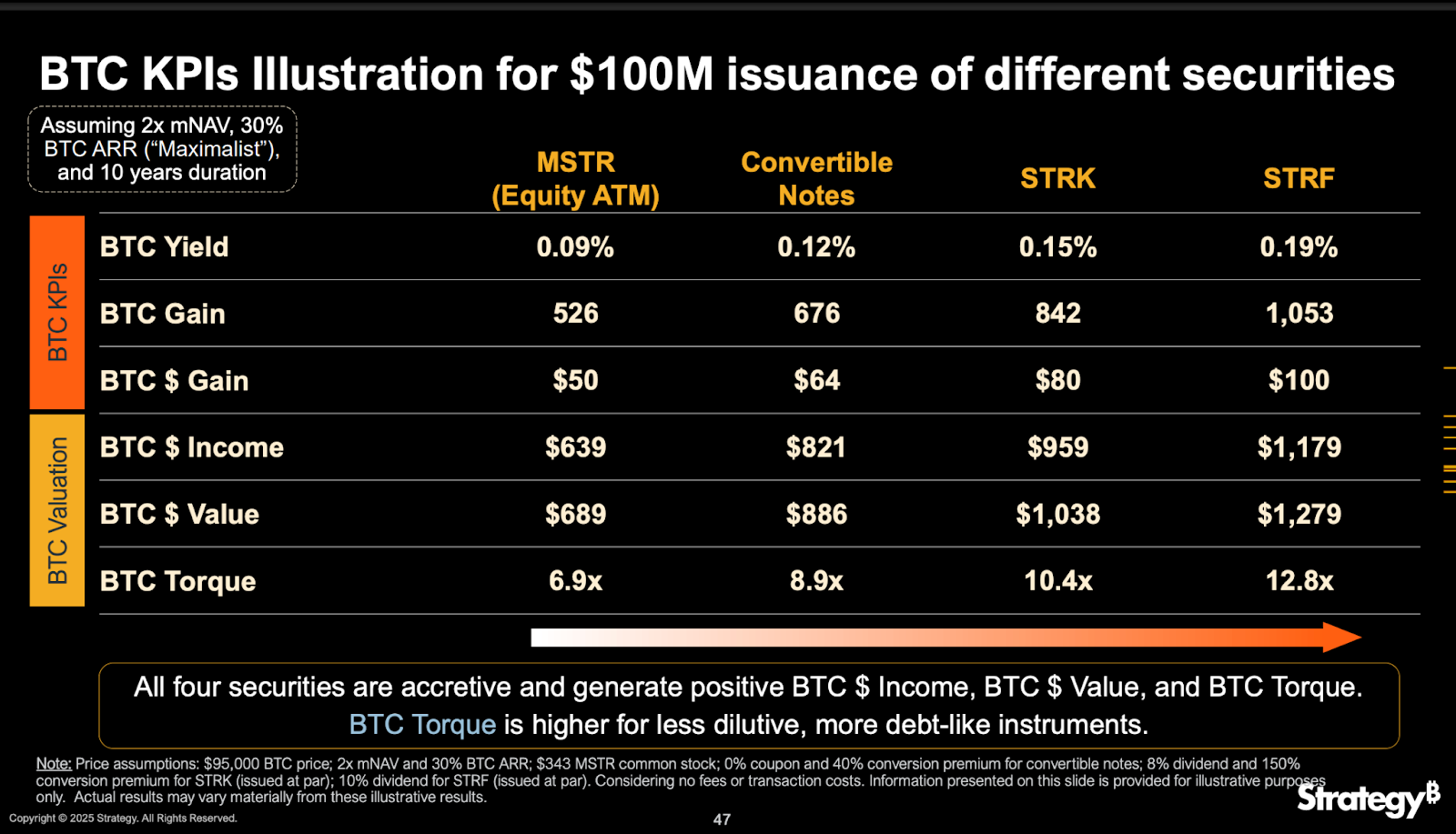
The data confirms that the less dilutive the capital instrument, the higher the BTC Torque it generates. Common equity, while a traditional financing method, is the most dilutive and produces the lowest BTC Torque at 6.9x. Convertible notes are less dilutive, generating a higher BTC Torque of 8.9x. However, the perpetual preferred stocks are the least dilutive and, as a result, consistently generate the highest BTC Torque. Under the "Maximalist" scenario, STRF, the most debt-like of the preferred securities, produces a remarkable 12.8x BTC Torque. This clear cause-and-effect relationship validates the company's strategic rationale for shifting its focus to perpetual preferreds. By using these intelligent leverage instruments, the company can acquire a greater amount of Bitcoin with less share dilution, thereby maximizing the value created for existing common shareholders.
3.2 The mNAV as a Strategic Barometer
The mNAV is more than a simple valuation metric; it functions as a live feedback mechanism for the company's capital allocation strategy. The company has established a rules-based framework for when to issue different types of securities, with mNAV serving as the primary guide.
The specific mNAV thresholds are as follows :
- Below 2.5x mNAV: The company will not issue common equity, except to cover debt interest, preferred dividends & when deemed advantageous to the company.
- Between 2.5x and 4.0x mNAV: The company will opportunistically issue common equity to acquire Bitcoin.
- Above 4.0x mNAV: The company will actively issue common equity to acquire Bitcoin.
- Below 1.0x mNAV: The company will consider using credit to repurchase its common stock.
This disciplined, rules-based framework creates a perpetual and self-adjusting value-creation loop. When the market's perception of the company's strategy is strong, reflected by a high mNAV, the company can issue highly accretive common equity to purchase more Bitcoin. This action, in turn, increases the BTC NAV, which further strengthens the balance sheet and enhances the creditworthiness of its preferred stocks. With this stronger foundation, the company can then issue more preferred stock, the very instruments that produce the highest BTC Torque to continue the cycle of value creation. This feedback loop demonstrates a level of strategic discipline that goes far beyond simply buying and holding an asset; it represents a sophisticated, self-optimizing financial system.
Section 4: Bitcoin as Pristine Collateral
4.1 The Over-Collateralization Thesis
The viability and appeal of the company's entire capital structure are underpinned by the enormous value of its Bitcoin treasury. This section quantifies Bitcoin's role as a superior form of collateral. As of July 29, 2025, the company held 628,791 bitcoins, with a BTC NAV of approximately $74 billion. This massive asset base underpins an enterprise value of approximately $126 billion, leaving a substantial $112 billion equity cushion for common shareholders after accounting for debt and preferred obligations. This demonstrates an unparalleled level of over-collateralization.
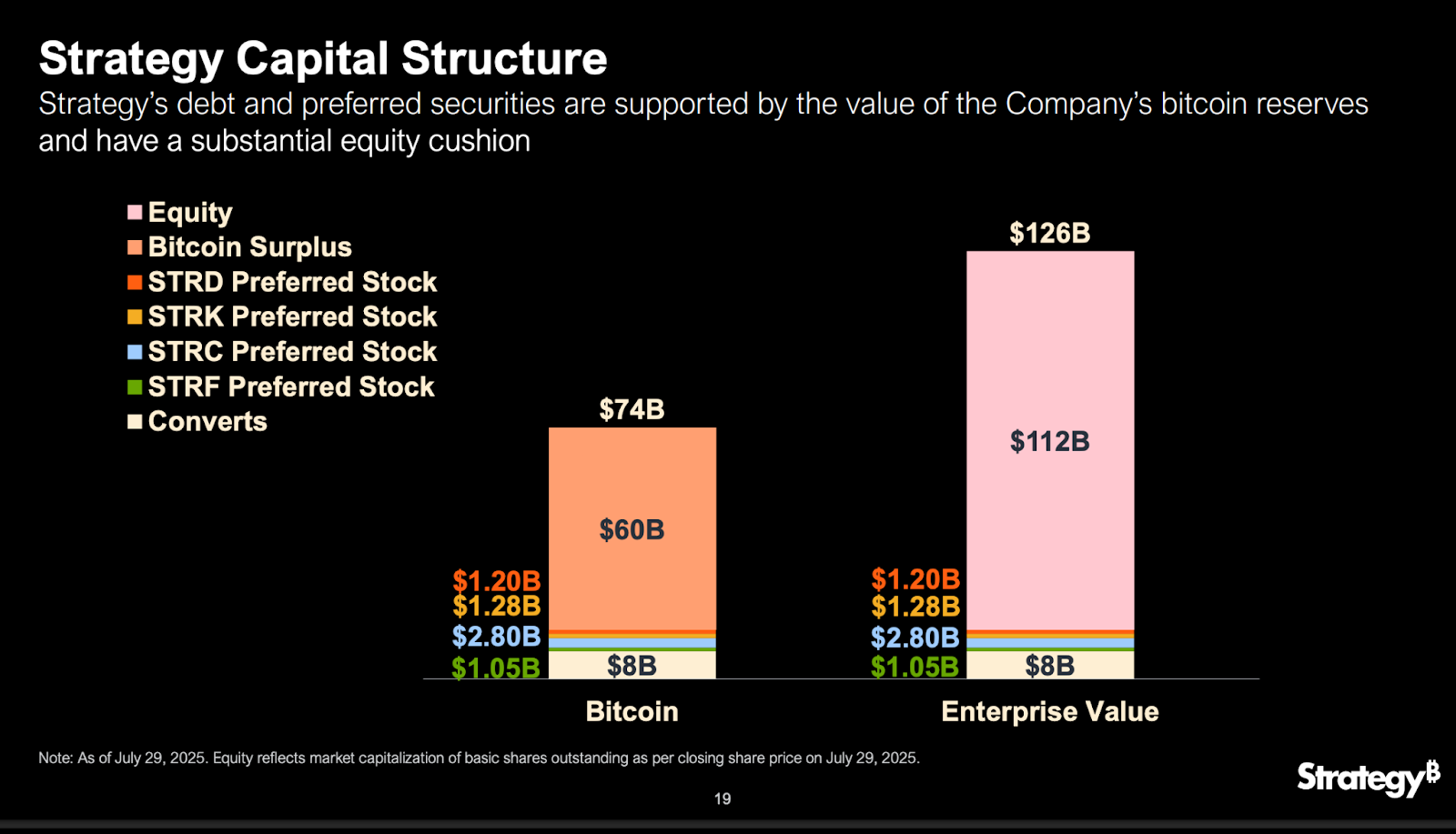
This over-collateralization provides an exceptional level of credit protection for all its securities. Unlike traditional corporate assets that can be illiquid or subject to operational and business risks, Bitcoin is a liquid, globally accessible, and fungible asset. The company's unique position as the world's largest corporate holder of this asset allows it to leverage its balance sheet in a way that few, if any, other companies can. This strategy effectively positions Bitcoin as a "pristine" form of collateral, providing a level of confidence to all stakeholders that surpasses that of traditional balance sheets.
Section 5: The Perpetual Preferred Stock Family: A Granular View
5.1 The STRC Perpetual Preferred Stock: A Quantifiable Advantage
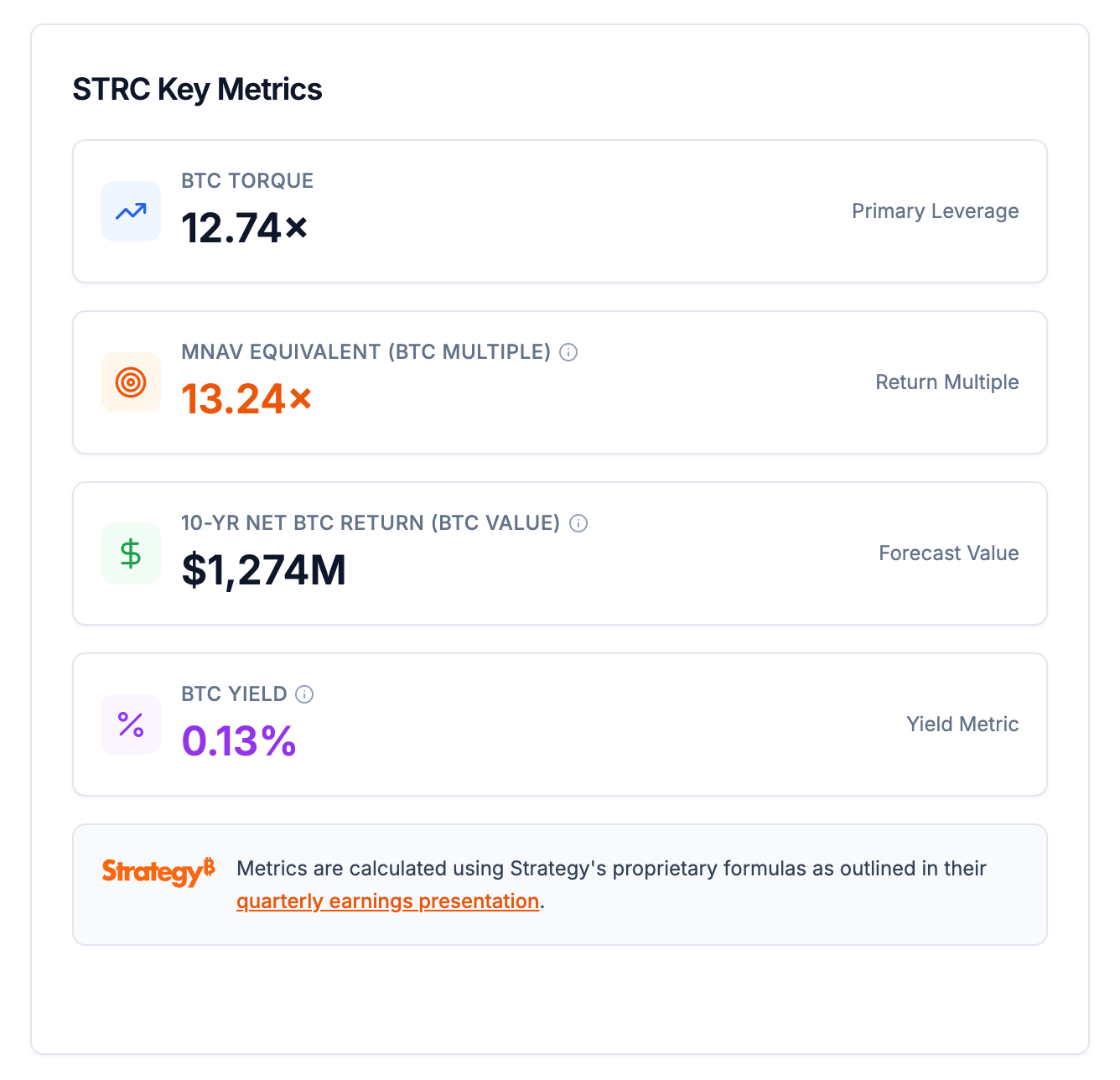
- To quantify the efficiency and potential of this instrument, the company has applied its proprietary financial models to STRC under a "Maximalist" scenario. The results highlight its superior performance compared to all other financing instruments, including common equity and convertible notes. The STRC security generates a BTC Torque of 12.74x. This figure is slightly higher than even the highly efficient STRF preferred stock, reaffirming that STRC is the most effective tool for generating value for common shareholders on a per-share basis.
The long-term value creation is further demonstrated by the mNAV Equivalent, also known as BTC Multiple, which for STRC is calculated at a remarkable 13.24x. This metric simulates the mNAV required for a common stock ATM to achieve the same cumulative BTC Gain and BTC Income as a STRC offering, underscoring the superior capital efficiency of the preferred stock model. A 10-year forecast model for STRC shows a significant growth in Bitcoin Net Asset Value, which is projected to reach over $1,274M , demonstrating the long-term value accretion. This growth is a result of the instrument's design to continuously add to the Bitcoin treasury, driven by the unique combination of BTC Equity, BTC Gain, and BTC Income components. The model also illustrates that STRC’s effectiveness, measured by its mNAV Equivalent, consistently increases over time, showcasing the long-term strategic advantage of this perpetual security.
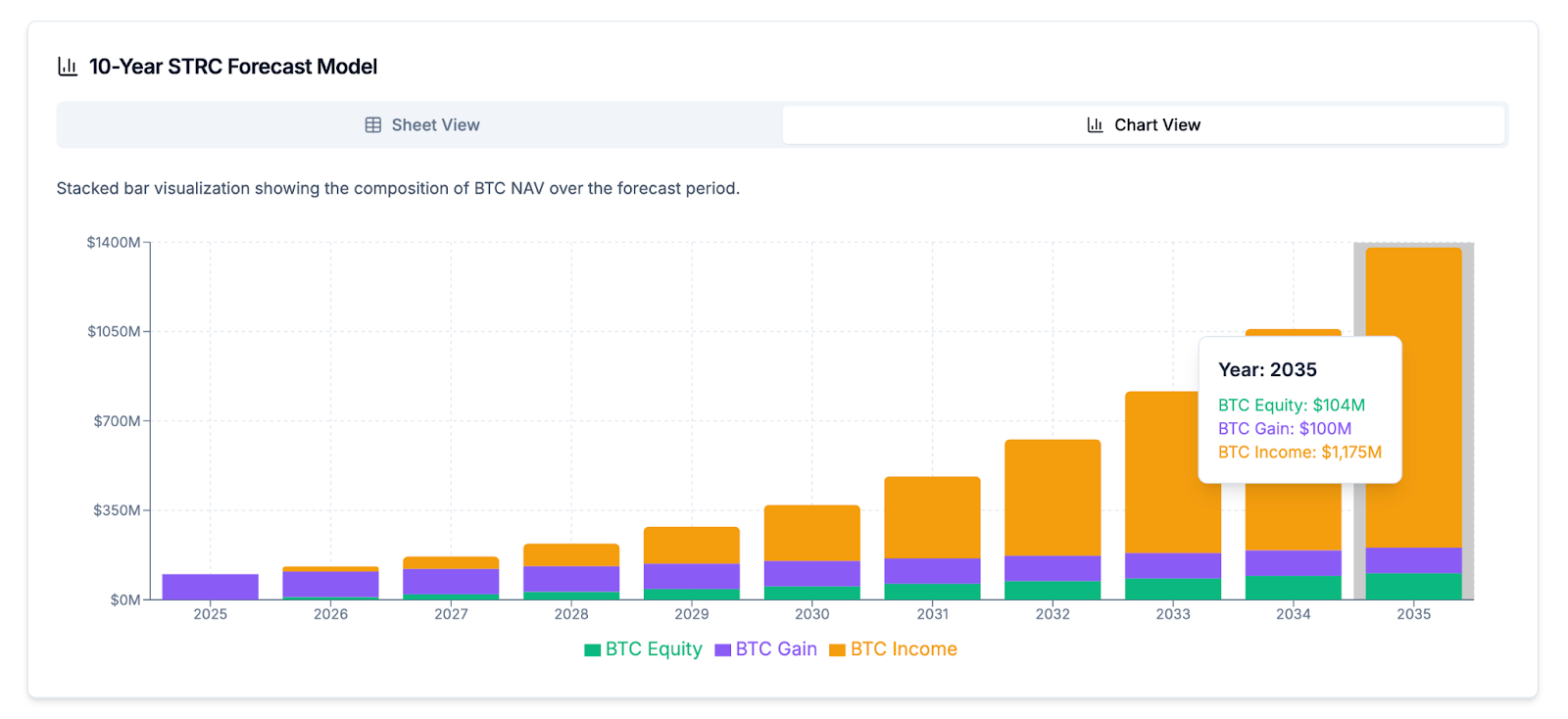
The STRC preferred stock is the latest and most refined instrument in the company's suite, specifically engineered to function as a "yield-enhanced savings account". It carries a variable, monthly dividend (10.25% annualized) and is designed to self-stabilize its price near its $100 par value. This security is intended for short-duration investors, offering a substantially higher yield than conventional instruments like money market funds and treasuries, while providing a unique blend of price stability and liquidity that occupies a "white-space niche" in the market.
5.2 The STRD Perpetual Preferred Stock: Quantifying its High-Yield Advantage
The STRD perpetual preferred stock is specifically designed to attract capital from the high-yield credit market. The company has applied its financial models to this security to quantify its value-creation capabilities. Key metrics for STRD under a "Maximalist" scenario show a BTC Torque of 12.56x, which is a powerful indicator of its capital efficiency. The mNAV Equivalent (or BTC Multiple) for STRD is calculated at 11.26x, which simulates the mNAV that a common stock ATM would need to achieve to match STRD's cumulative BTC Gain and BTC Income.
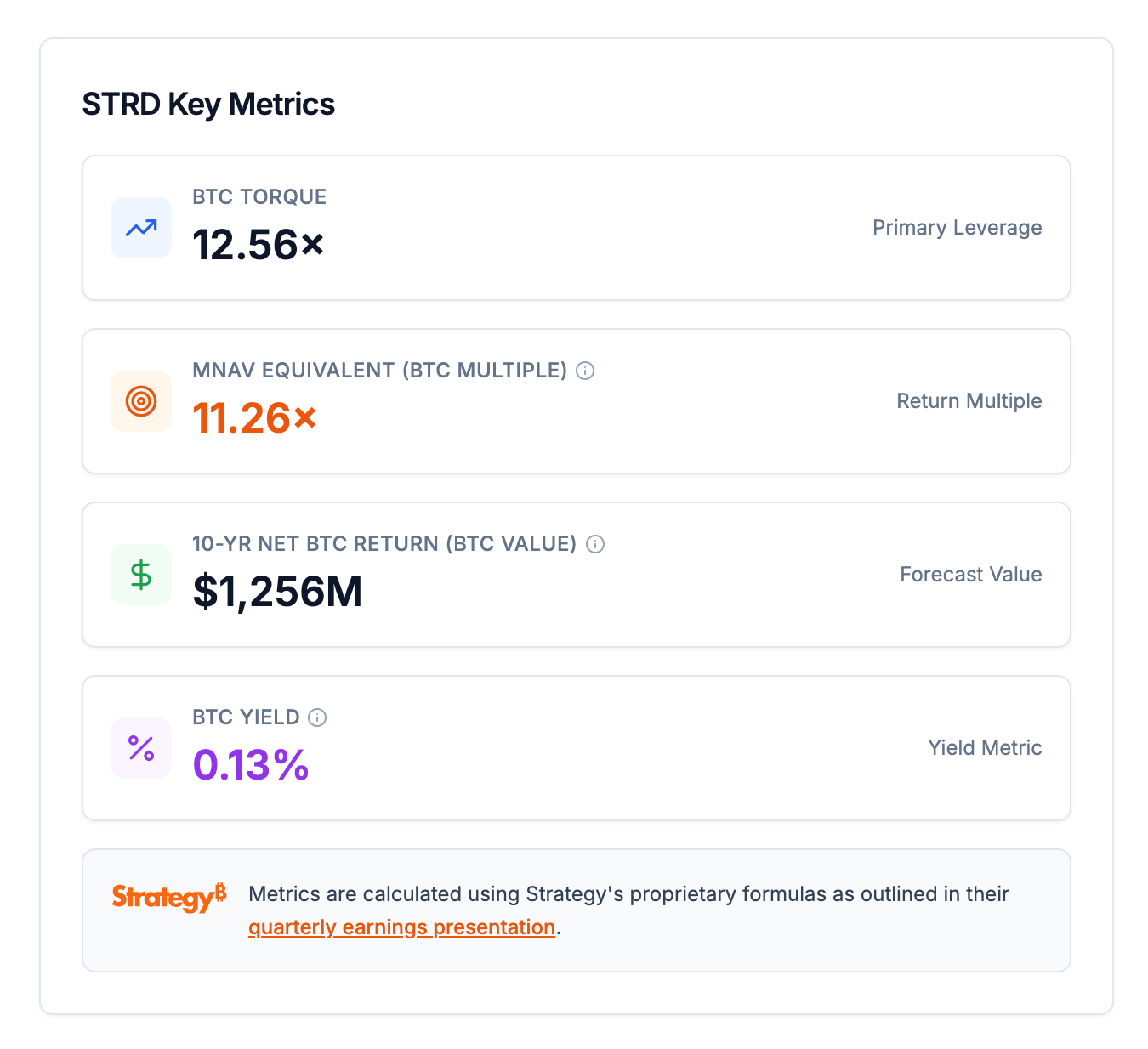
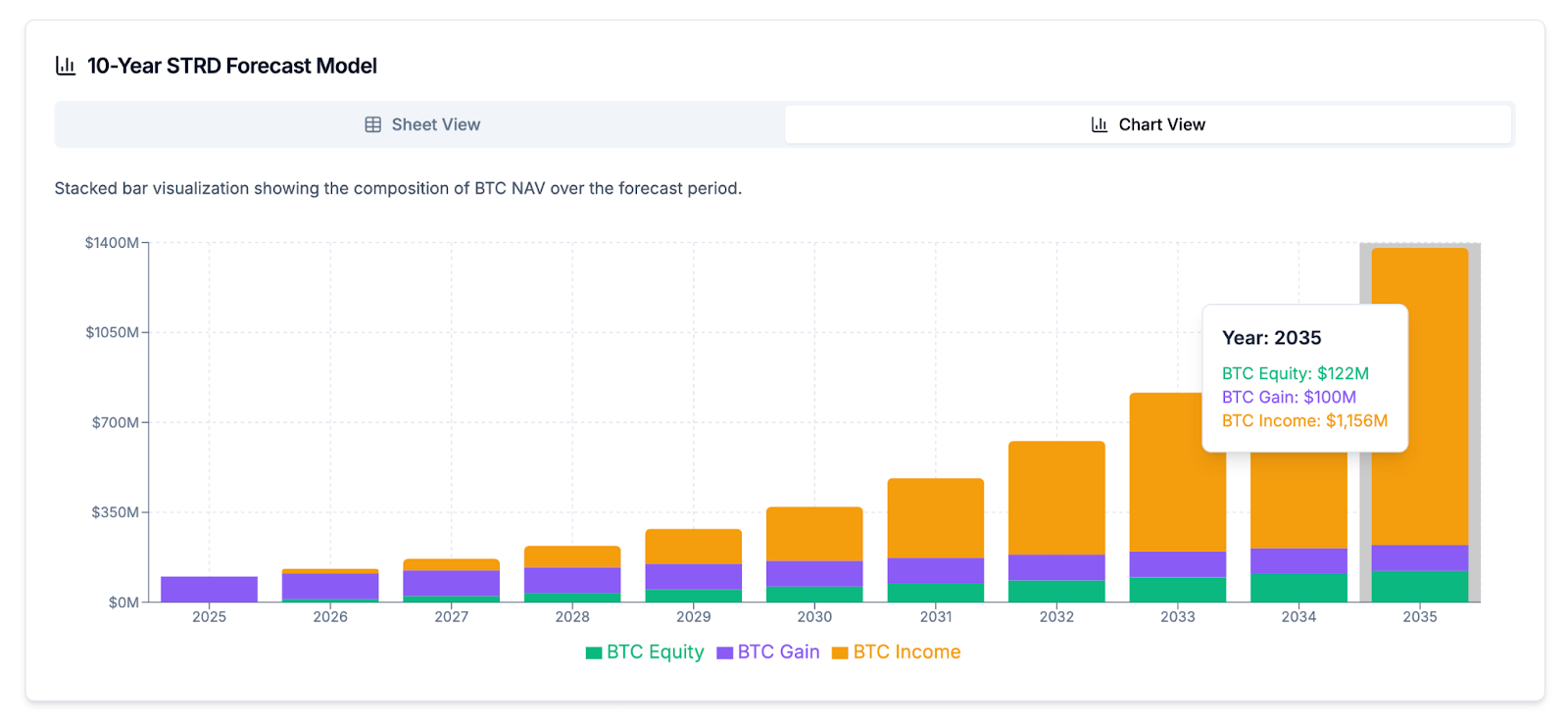
A 10-year forecast model for STRD projects a net Bitcoin return of $1,256M, which showcases the long-term value creation potential of this instrument. The forecast model demonstrates how STRD contributes to the overall growth of Bitcoin Net Asset Value over the forecast period. The mNAV Equivalent graph for STRD further illustrates its long-term strategic advantage by showing a consistent increase in its effectiveness over time.
5.3 The STRK Perpetual Preferred Stock: Quantifying the Growth-Oriented Hybrid
The STRK preferred stock is a unique hybrid security that combines a fixed 8% dividend with a conversion right into the company's common stock, targeting growth-oriented income investors. The company's financial models quantify STRK's value-creation capabilities, demonstrating its strategic position in the tiered suite of perpetual preferred stocks.Under a "Maximalist" scenario, the STRK security generates a BTC Torque of 9.73x. While this is lower than the more debt-like STRC and STRD securities, it is significantly higher than the BTC Torque generated by common equity and even traditional convertible notes, validating its capital efficiency.
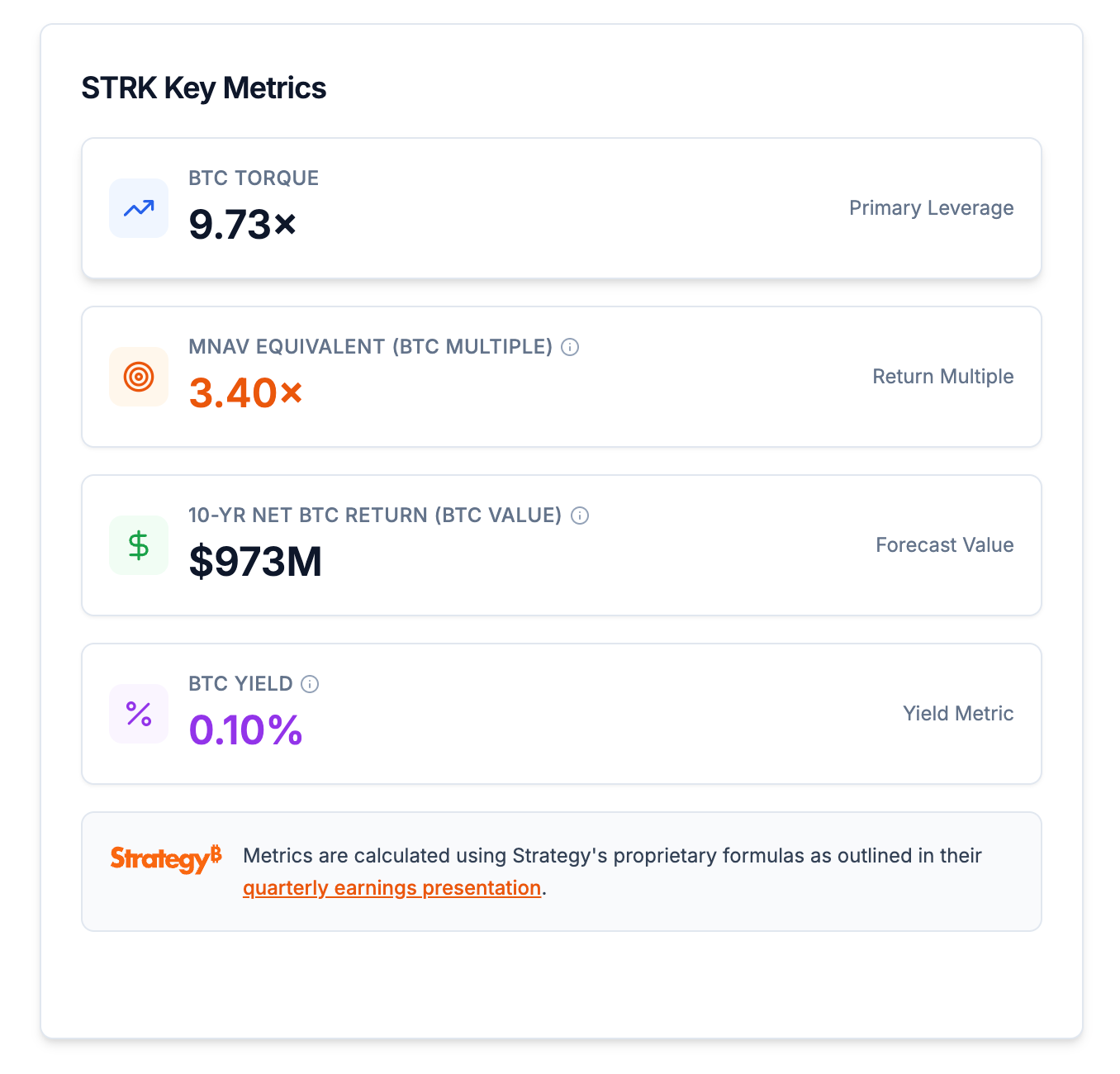
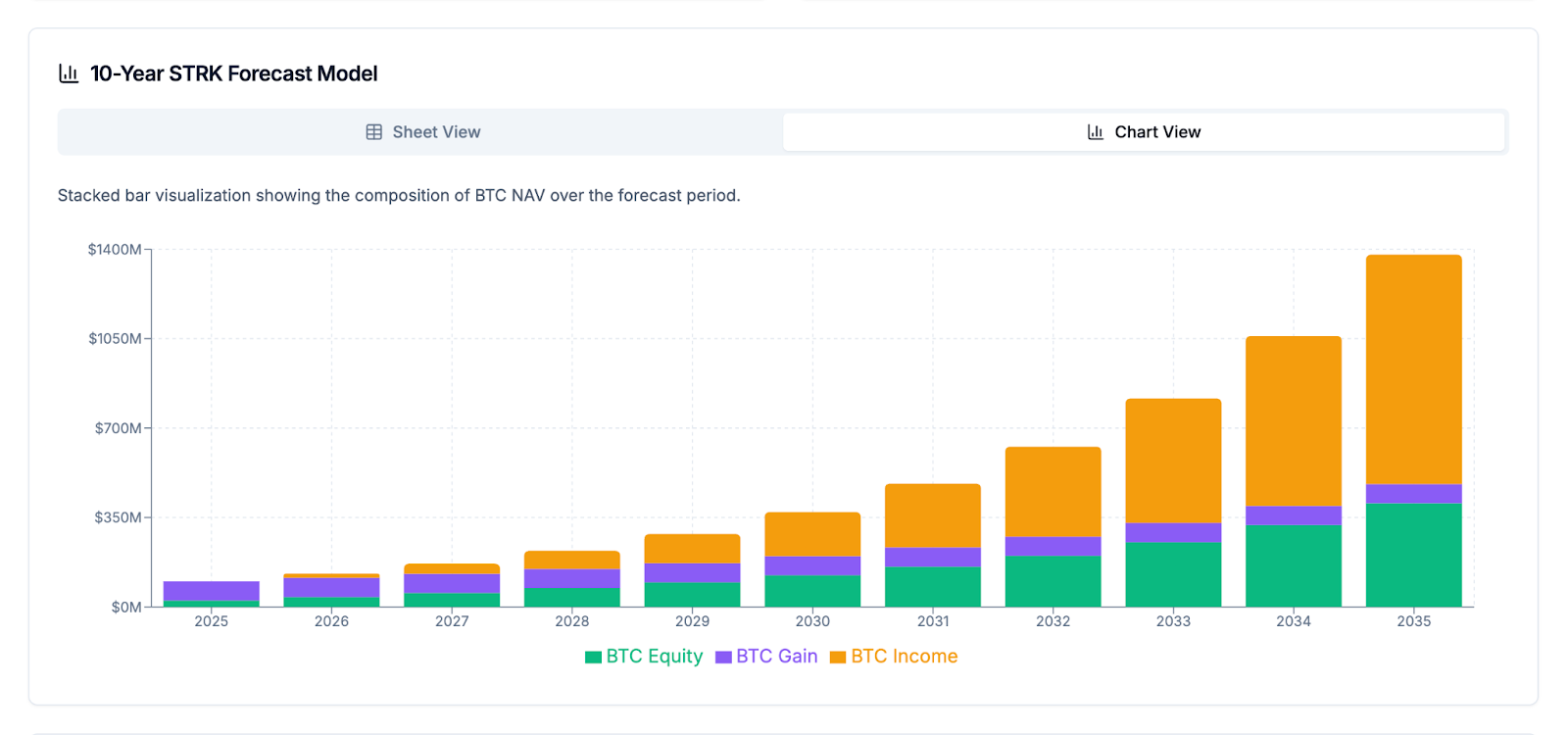
The long-term value is further illustrated by its mNAV Equivalent (or BTC Multiple) of 3.40x, a metric that simulates the mNAV a common stock ATM would require to achieve the same cumulative BTC Gain and BTC Income as STRK. This metric, when viewed over a 10-year forecast, shows a consistent increase in
STRK's effectiveness over time. The 10-year forecast model also projects a net Bitcoin return (BTC Value) of $973M, showcasing the instrument’s long-term value accretion. The forecast demonstrates a continuous growth in Bitcoin Net Asset Value, composed of
BTC Equity, BTC Gain, and BTC Income components, highlighting STRK's contribution to the overall growth of the Bitcoin treasury.
5.5 The STRF Perpetual Preferred Stock: Quantifying its Senior Credit Advantage
STRF is a perpetual preferred stock designed to attract investors from the long-duration, investment-grade credit markets. It offers a fixed 10% cash dividend with enhanced payment protection features, positioning it as a compelling alternative for income-focused investors.
The STRF preferred stock is a key component of the company's capital structure, designed to appeal to investors in the long-duration, investment-grade credit markets. The company's proprietary financial models have been applied to STRF to quantify its value-creation potential under a "Maximalist" scenario.
Key metrics for STRF reveal its superior capital efficiency. It generates a BTC Torque of 12.92x, which is a powerful indicator of how effectively it leverages capital to create shareholder value.The mNAV Equivalent (or BTC Multiple) for STRF is calculated at a remarkable 15.84x, simulating the mNAV required for a common stock ATM to achieve the same cumulative BTC Gain and BTC Income. This demonstrates that STRF is an extremely capital-efficient instrument.
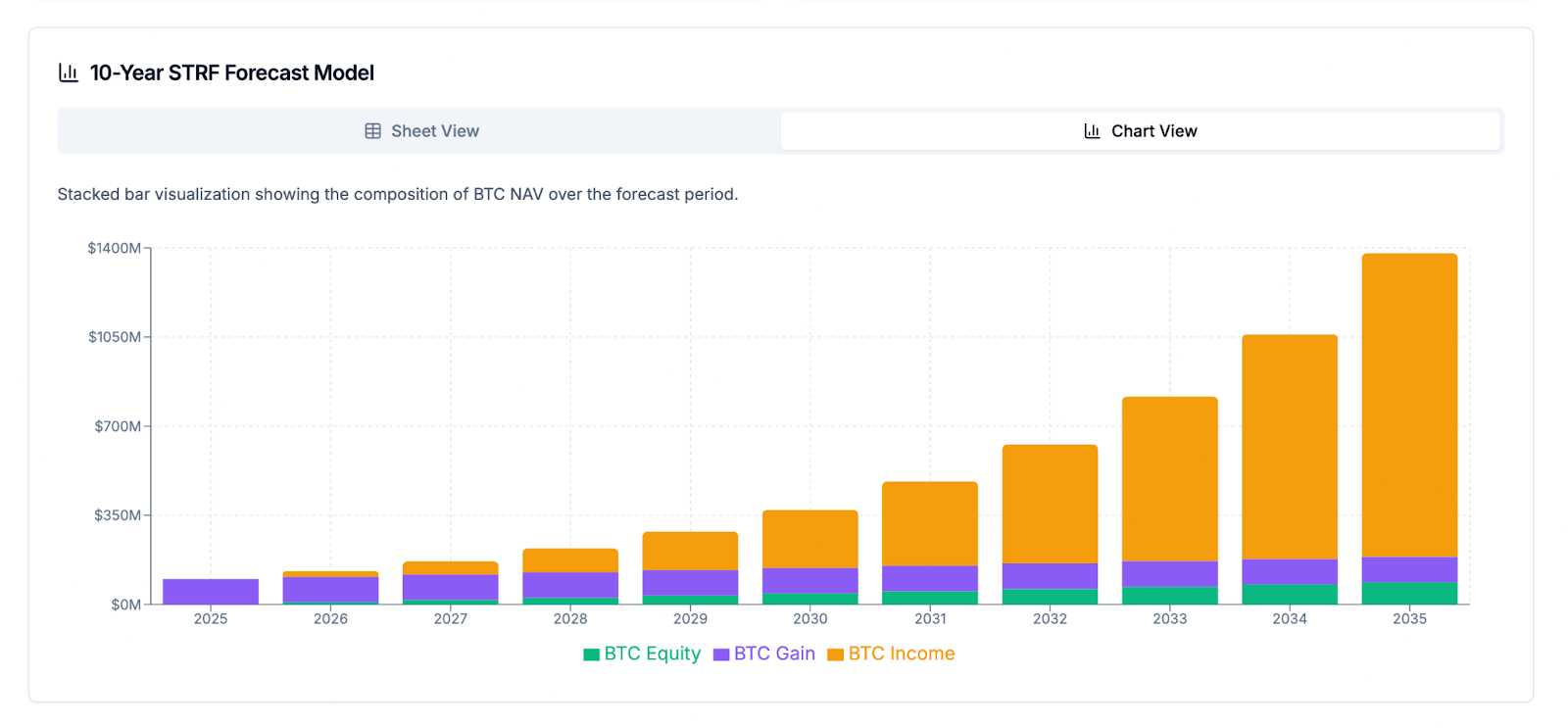
A 10-year forecast model for STRF projects a net Bitcoin return (BTC Value) of $1,292M, highlighting its significant contribution to long-term value accretion. The forecast model also visually demonstrates the growth in the Bitcoin Net Asset Value over the forecast period, driven by the unique combination of
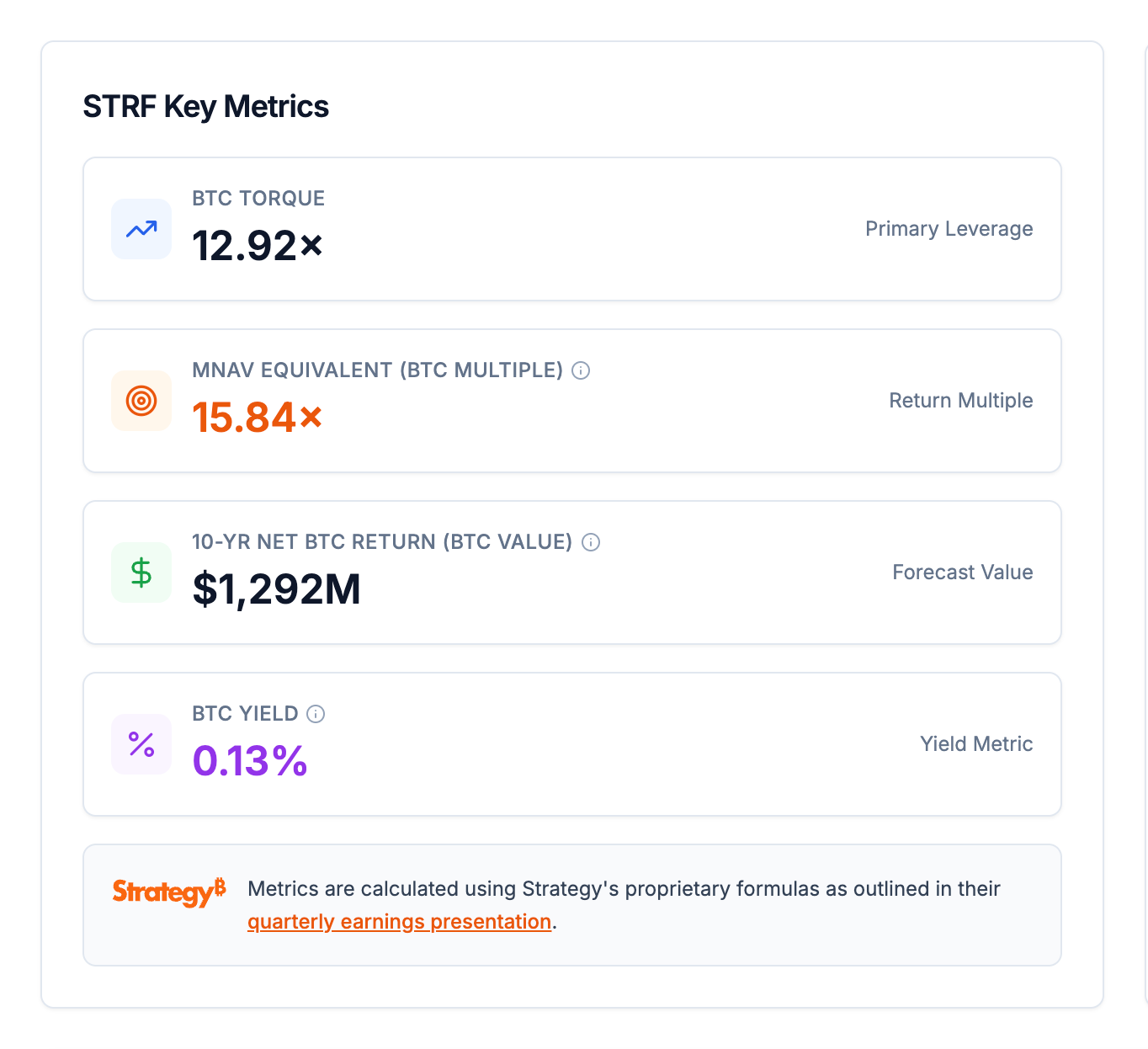
BTC Equity, BTC Gain, and BTC Income components. The mNAV Equivalent graph further illustrates the long-term strategic advantage, showing a consistent increase in its effectiveness over time.
Section 6: Strategic Implications and Conclusion
6.1 A Blueprint for Corporate Finance
The company has successfully moved beyond the simple accumulation of Bitcoin to a sophisticated financial strategy that systematically and sustainably leverages its pristine collateral. This model, with its emphasis on transparency, capital efficiency, and risk mitigation, could serve as a blueprint for a new era of corporate finance. The reliance on proprietary metrics, such as mNAV and BTC Torque, and a rules-based capital allocation framework provides a level of strategic discipline that is uncommon in the corporate world. This approach minimizes subjective decision-making and offers a clear, defensible long-term strategy for investors to evaluate.




