Financing Strategies for BTCTCs Under Sub-NAV Valuation Conditions

Executive Summary
Bitcoin Treasury Companies (BTCTCs) operate with a financial objective distinct from traditional corporations long-term maximisation of Bitcoin per Share (BPS). Their balance sheets function primarily as Bitcoin reserve portfolios, and the integrity of these reserves determines their strategic position across market cycles.
When BTCTC equity trades below monetary net asset value (mNAV < 1) meaning market capitalization is lower than the fair value of Bitcoin held on the balance sheet capital markets access becomes structurally constrained. Equity issuance becomes value-destructive, conventional convertibles become mispriced, and many financing tools create permanent impairment to BPS.
This analysis focuses exclusively on the financing options that remain strategically viable under sub-NAV valuation conditions and provides institutional-grade insight into instrument mechanics, investor incentives, risk considerations, and cycle-appropriate deployment.
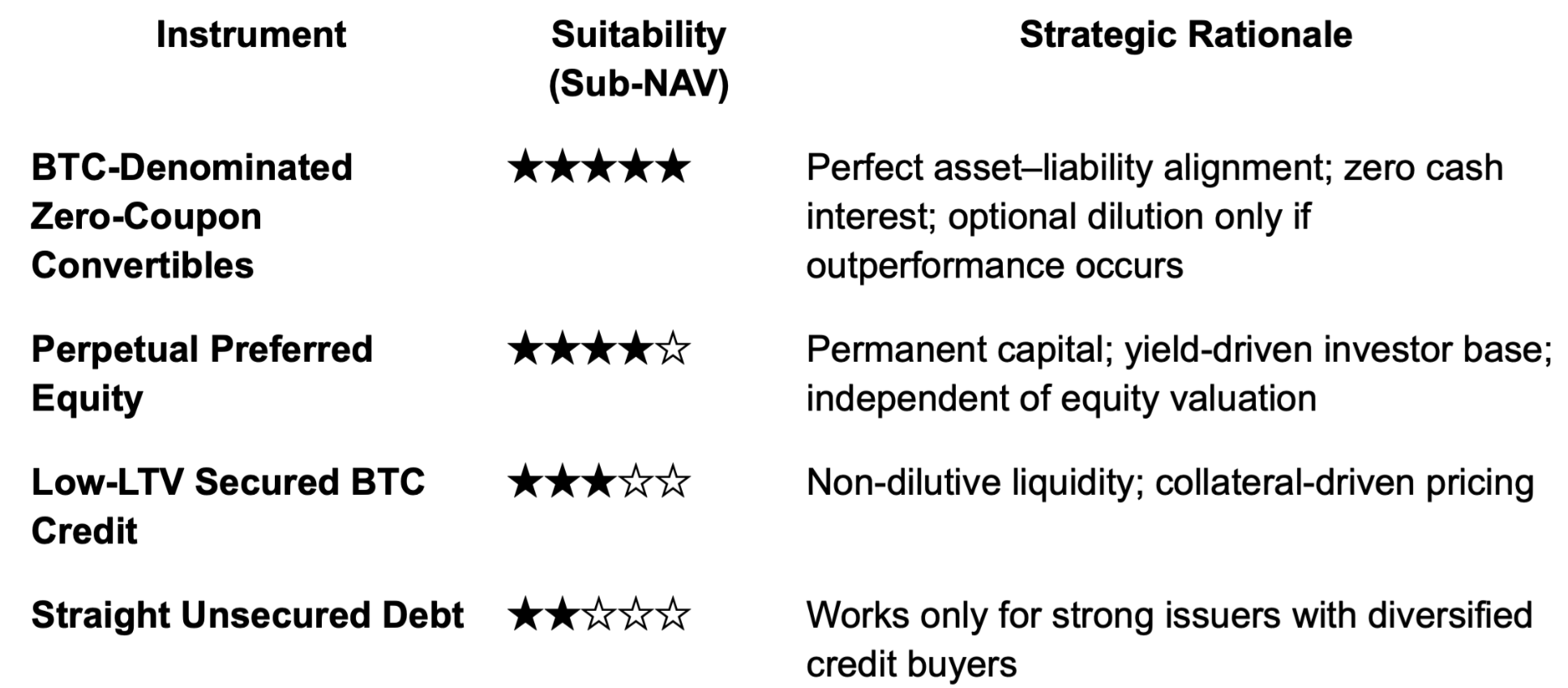
The relevant financing tools under these circumstances are:
- BTC-denominated zero-coupon convertible bonds
- Perpetual preferred equity
- Low-LTV secured Bitcoin credit facilities
- Long-term straight debt (unsecured bonds)
Each of these instruments can support liquidity and duration without compromising treasury integrity provided they are structured and sequenced correctly.
Market Context: Implications of Sub-NAV Trading Levels
Trading below NAV signals that markets are discounting:
- The value of the company’s Bitcoin treasury
- Management’s near-term ability to add incremental BTC per share
- Liquidity availability and balance sheet buffers
- Execution risk around capital allocation
Under these conditions:
- Equity issuance transmits value away from existing shareholders
- Hybrid instruments reliant on equity valuation become mispriced
- Credit costs rise due to BTC volatility and reduced equity cushion
- Arbitrageurs dominate trading flows
The capital stack must shift from growth-mode issuance to duration defense, liquidity protection, and BPS preservation.
Only financing tools not directly anchored to common equity valuation remain usable.
Bitcoin-Denominated Convertible Bonds
The most structurally aligned capital instrument for BTCTCs under valuation stress
Mechanics
A Bitcoin-denominated zero-coupon convertible note is a BTC-native financing structure with three defining components:
- Principal lent in BTC
- No coupon 0% interest cost
- At maturity:
- Investor converts to equity → BTC becomes permanent treasury
- OR investor receives the same BTC back
Conversion is set in at a pre-determined share price which is attractive to both the company and the investor.
The instrument behaves economically like a BTC-collateralized call option on the company's equity.
Investor Profile
- Long-term Bitcoin holders
- Bitcoin-native funds
- Bitcoin family offices
- Treasury allocators with BTC mandates
These investors seek BTC-linked upside with capital preservation.
Why It Works Sub-NAV
- No dilution unless the company outperforms Bitcoin
- No short selling (unlike fiat convertibles)
- No refinancing wall risk
- Liability denominated in the same asset as the treasury
- Zero cash interest expense
- Value transfer aligns with BTC-adjusted performance
This structure is economically and philosophically consistent with BTCTC balance sheets.
Risk Considerations
- Potential for equity dilution in a bull cycle
- BTC liquidity management required for repayment
- Limited participation from traditional credit funds
Perpetual Preferred Equity
Permanent capital with no refinancing risk
Mechanics
- Fixed or floating dividend
- No contractual maturity
- Senior to common equity
- No obligation to redeem principalPreferred equity behaves like high-duration, yield-oriented capital. Investor Profile
- Yield-focused institutional funds
- Insurance companies
- Pension investors
- Multi-asset income strategies
- Credit-oriented hedge funds
They value yield and seniority, not spot equity valuation.
Why It Works Sub-NAV
- Investors assess dividend coverage and balance sheet quality not NAV discount
- No short-selling pressure
- No maturity-driven refinancing risk
- Long-term stability improves credit profile
Preferred equity can raise capital independent of common equity valuation, making it uniquely effective when mNAV < 1.
Risk Considerations
- Fixed dividend obligations must be modeled across BTC volatility cycles
- Accrued dividends worsen leverage optics
- Secondary liquidity may be thin
Secured Bitcoin Credit Lines
Non-dilutive liquidity if executed with strict risk discipline
Mechanics
- BTC posted as collateral
- Loan-to-value (LTV) typically 10–30%
- Floating interest rate
- Short to medium tenor (6–18 months)
- Custodial collateral management
Investor/Lender Profile
- Crypto credit funds
- Digital asset prime brokers
- Structured credit desks
- Crypto custodians with lending programs
These lenders evaluate collateral quality, not equity valuation.
Why It Works Sub-NAV
- Provides liquidity without equity dilution
- Pricing driven by BTC volatility, not issuer valuation
- Effective for operational runway or tactical BTC accumulation
- Flexible and fast compared to unsecured markets
Risk Considerations
- Margin call risk
- Forced BTC liquidation during volatility
- LTV tightening in market shocks
- Counterparty concentration risk
BTCTCs must employ conservative LTVs and maintain redundant liquidity buffers.
Straight Debt (Long-Term Unsecured Bonds)
Partially viable for strong issuers; credit-driven, not equity-driven
Mechanics
- Unsecured corporate bonds
- Fixed or floating coupon
- 5–10 year maturities
- Fully repayable in fiat
- No collateral
Investor Profile
- Global high-yield funds
- Multi-strategy credit investors
- Cross-over buyers
- Insurance companies (selectively)
Why It Can Work Sub-NAV
For strong, seasoned BTCTCs (e.g., Strategy/MicroStrategy), unsecured bonds may still be feasible because:
- Debt investors evaluate coverage, liquidity, and asset stability, not equity valuation
- BTC treasury acts as an implicit reserve
- Issuers with favorable credit histories retain market access
Risk Considerations
- Coupons rise sharply when mNAV < 1
- Fiat-denominated obligations mismatch BTC-denominated reserves
- Maturity walls introduce refinancing risk
- Rating agencies penalize BTC concentration
For smaller or newer BTCTCs, this instrument is often inaccessible or uneconomical in downcycles.
Final Synthesis
For BTCTCs trading below NAV, the legitimate financing toolkit narrows to four options:
Every other capital tool ATMs, PIPEs, follow-ons, equity-linked fiat convertibles should be avoided entirely until mNAV normalizes.
Conclusion
A Bitcoin Treasury Company operating below NAV must prioritize treasury preservation, duration extension, and disciplined capital structuring. Only a narrow subset of financing instruments align with these objectives. By relying on BTC-native convertibles, carefully structured preferred equity, conservative secured credit, and selectively accessed long-term debt, BTCTCs can maintain financial integrity while positioning themselves for asymmetric upside in the next Bitcoin cycle.
The future winners will be those that protect Bitcoin per Share, avoid dilution during NAV discounts, and adopt Bitcoin-native financing structures that reflect the monetary nature of their balance sheets.
FOLLOW US ON:
X (Twitter), Youtube, Instagram, Linkedin
Access to these products and services is restricted to non-U.S. persons and may not be available in certain jurisdictions.




