Digital Money: The Final Layer of the Bitcoin Financial Stack


Introduction: Why the World Still Lacks “Good Money”
For over a decade, Bitcoin has proven itself as digital capital, a scarce, global, censorship-resistant store of value. It has absorbed volatility, rewarded long-term holders, and increasingly sits on corporate and institutional balance sheets.
Yet despite Bitcoin’s success, one core problem remains unresolved:
Bitcoin is not yet “money” for everyday economic coordination.
Not because it fails conceptually but because money is a system, not a single asset.
Modern economies require instruments that:
- Hold stable purchasing power in the short term
- Can be used as a unit of account
- Enable frictionless payments and settlement
- Preserve value relative to inflation
Bitcoin excels as long-term capital, but its volatility makes it impractical as day-to-day money. Fiat currencies, meanwhile, function well operationally but fail structurally due to debasement, credit expansion, and political control.
This gap between hard money and usable money is where Digital Money emerges.
The Three-Layer Bitcoin Monetary Stack
To understand Digital Money, we must first understand the stacked architecture of a Bitcoin-native financial system.
Layer 1: Digital Capital (Bitcoin)
Bitcoin is the base layer:
- Fixed supply
- No issuer
- No dilution
- Global settlement
- High volatility, but high long-term appreciation
Bitcoin functions like digital gold, or more accurately, digital capital, an asset optimized for long-term wealth preservation, not transactional stability.
Layer 2: Digital Credit (Bitcoin-Backed Instruments)
Digital credit sits on top of Bitcoin.
Here, Bitcoin is used as collateral to issue:
- Over-collateralized notes
- Preferred equity
- Convertible instruments
- Structured credit products
The purpose of digital credit is to:
- Reduce volatility relative to Bitcoin
- Extract yield from Bitcoin’s monetary properties
- Enable capital formation without selling BTC
Bitcoin Treasury Companies (BTCTCs) like Strategy, Metaplanet, and others operate primarily at this layer.
Digital credit is less volatile than Bitcoin, but still not stable enough to function as money.
Layer 3: Digital Money (The Missing Layer)
Digital Money is the final abstraction.
It is:
- Stable in nominal value (≈ $1)
- Yield-bearing
- Highly liquid
- Built on top of digital credit
Digital Money is not Bitcoin and it does not compete with Bitcoin.
Instead, it allows Bitcoin to become the base asset of a monetary system without forcing users to tolerate volatility.
What Is Digital Money?
Digital Money is a Bitcoin-native monetary instrument designed to behave like cash while being powered by Bitcoin-backed credit.
In practical terms, Digital Money aims to achieve:
- Stable NAV (≈ $1)
- Daily liquidity
- Meaningfully higher yield than traditional money markets
- No reliance on fractional banking
Think of it as a Bitcoin-anchored money market instrument.
Not a speculative asset. Not a volatile token. Not a fiat stablecoin backed purely by Treasuries.
But a new category entirely.
How Digital Money Is Engineered
Digital Money is not created by decree. It is engineered through portfolio construction, buffers, and discipline.
Core Portfolio Structure
A representative Digital Money portfolio might look like:
- ~80% Digital Credit
- Bitcoin-backed, over-collateralized instruments like STRC & SATA
- Designed to deliver high, durable yield
- ~20% Currency Equivalents
- T-Bills, cash-like instruments, or high-quality stable reserves
- Additional Reserve Buffer (~10%)
- Used explicitly to absorb volatility and protect the $1 NAV
This structure mirrors the logic of traditional money-market funds but replaces sovereign credit with Bitcoin-backed credit.
The Role of the Reserve Buffer
The reserve buffer is critical.
It serves as:
- A volatility shock absorber
- A liquidity backstop during redemptions
- A credibility mechanism for maintaining a stable NAV
When the digital credit sleeve fluctuates in value:
- The buffer absorbs short-term mark-to-market moves
- Yield can be skimmed to replenish reserves over time
This allows the instrument to feel like cash, even though it is built on Bitcoin.
Yield: Why Digital Money Can Pay More
Traditional money markets earn yield from:
- Sovereign debt
- Bank balance sheets
- Central-bank policy rates
Digital Money earns yield from:
- Bitcoin-backed credit
- Over-collateralization
- Structural scarcity of Bitcoin
Because Bitcoin is:
- Finite
- Highly liquid
- Globally demanded
Credit built on Bitcoin can command yields structurally higher than fiat credit without relying on inflation or leverage.
Even after accounting for:
- Reserve drag
- Liquidity buffers
- Conservative risk management
Digital Money can plausibly deliver several hundred basis points more than traditional cash instruments.
Forms Digital Money Can Take
Digital Money is not limited to crypto rails.
It can exist as:
1. A Digital Money Token
- Stablecoin-like structure
- On-chain settlement
- $1 NAV
- Yield distributed via staking or dividends
2. A Digital Money Fund or ETF
- Regulated wrapper
- Distributed via brokerage accounts
- Stable NAV
- Familiar to institutional investors
3. A Digital Money Bank Account
- Deposit-like experience
- Daily yield
- Fiat on-ramps and off-ramps
- “Bitcoin-powered savings account”
This flexibility is intentional.
Digital Money is not about ideology, it's about distribution at scale.
Why Digital Money Matters
For Individuals
- Preserve purchasing power without volatility
- Earn real yield on cash
- Exit fragile banking systems without going “full Bitcoin”
For Institutions
- Park liquidity without holding debasing fiat
- Access Bitcoin-linked yield with minimal volatility
- Replace money-market funds with superior instruments
For Bitcoin Itself
- Expands Bitcoin’s role from asset → system
- Enables everyday economic use without compromising hardness
- Allows Bitcoin to underwrite global finance without being spent
Digital Money allows Bitcoin to remain untouched capital while still powering the monetary layer above it.
Risks and Constraints
Digital Money is not risk-free.
Key risks include:
- Liquidity mismatches during extreme stress
- Regulatory classification and approval
- Credit instrument failure
- Custody and operational risk
However, these risks are structural and analyzable, unlike fiat debasement which is guaranteed.
The goal of Digital Money is not perfection. It is superiority on a risk-adjusted basis.
The Endgame: Bitcoin as the Base of the Monetary Pyramid
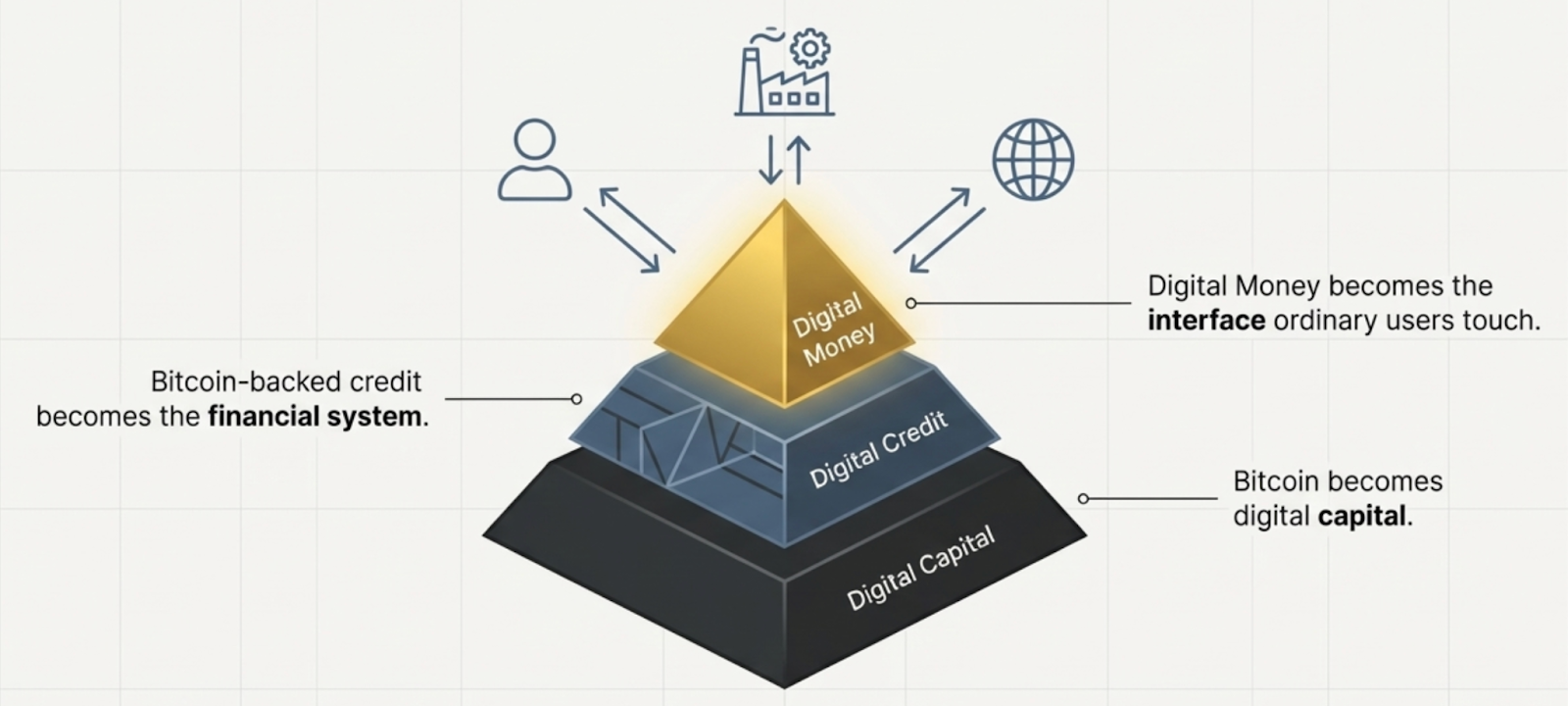
Bitcoin does not need to replace money.
It needs to replace the foundation beneath money.
Digital Money is how that happens.
- Bitcoin becomes digital capital
- Bitcoin-backed credit becomes the financial system
- Digital Money becomes the interface ordinary users touch
This is not a revolution it is an evolution.
And it may represent the most important step in Bitcoin’s journey yet.
FOLLOW US ON:
X (Twitter), Youtube, Instagram, Linkedin
Access to these products and services is restricted to non-U.S. persons and may not be available in certain jurisdictions.




